
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
2023-07-30
With the continuous development of industry, the use of steel is also increasing. However, during the production process or finished product storage process, steel sheets are prone to oxidation and rust when encountering humid air and rainy days, which affects the appearance quality of products. This has brought problems to the use of steel, and the annual loss of steel caused by corrosion is astonishing.

Metals are divided into non-ferrous metals and Ferrous, and Ferrous include iron, manganese and chromium. Iron is hard and ductile, has strong ferromagnetism, good plasticity and thermal conductivity, and is widely distributed on Earth. Various alloys based on iron, including cast iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, etc., are widely used.

1. Ferrous water-based rust inhibitor
The water-based antirust agent for Ferrous generally consists of Corrosion Inhibitor, complexing agent, alkali, wetting agent, etc. The substance that plays a core role in the rust prevention process is corrosion inhibitor, and different corrosion inhibitors have different corrosion inhibition mechanisms. Different combinations of corrosion inhibitors result in significant differences in rust prevention performance.Common inorganic corrosion inhibitors include Sodium nitrite, Sodium molybdate, Sodium tungstate, boric acid, borax, phosphate, etc. They are all anodic oxidation inhibitors. There are more kinds of organic corrosion inhibitors, such as well-known carboxylic acid salts: monocarboxylic acid, dicarboxylic acid, ternary acid, etc. In addition, fatty acid amides, borate esters, petroleum sulfonates, alkyl succinic acid, cationic Quaternary ammonium cation salts, etc. This type of corrosion inhibitor contains elements with lone pair electrons such as nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and oxygen, and can directly form a chemical adsorption layer on the metal surface. It belongs to the mixed type of corrosion inhibitor.

The analysis of Ferrous rust inhibitor plays an important role in the research and development of rust inhibitor.
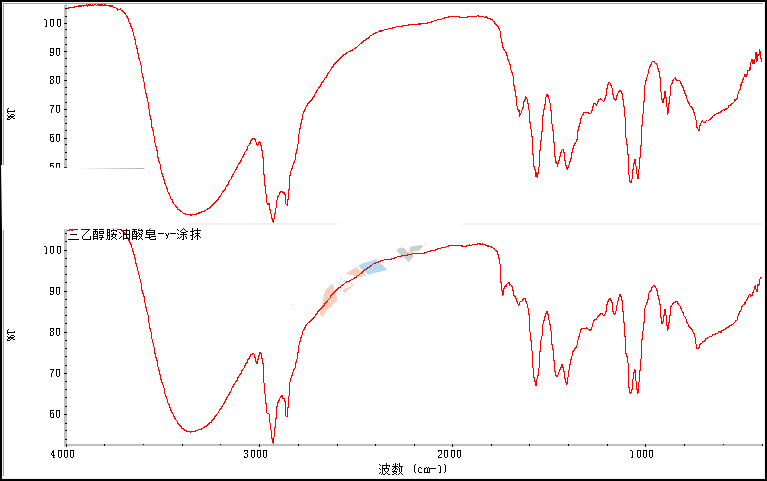
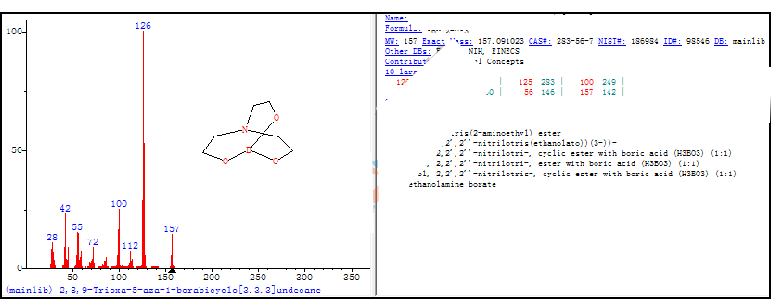
Infrared spectroscopy IR
Infrared spectroscopy is widely used for qualitative analysis of small molecules and polymer compounds, which is a relatively simple and fast analysis method. Figure 1 is the infrared matching spectrum of an unknown substance. Through the matching spectrum, we can know that the unknown substance is Triethanolamine oleate soap, which belongs to monobasic Carboxylate.
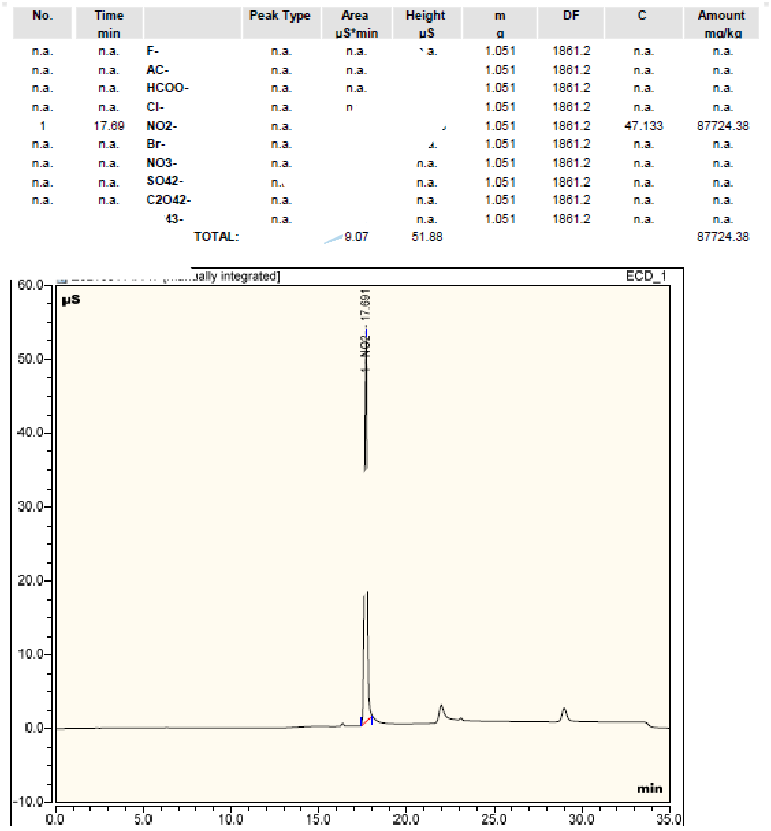
Nuclear magnetic resonance instrument NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance can analyze and test corrosion inhibitors in rust inhibitors. Figure 2 shows the 1H-NMR spectrum of a corrosion inhibitor.
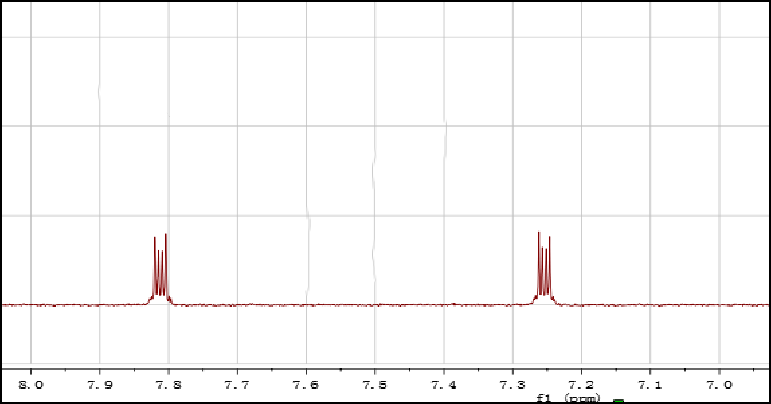
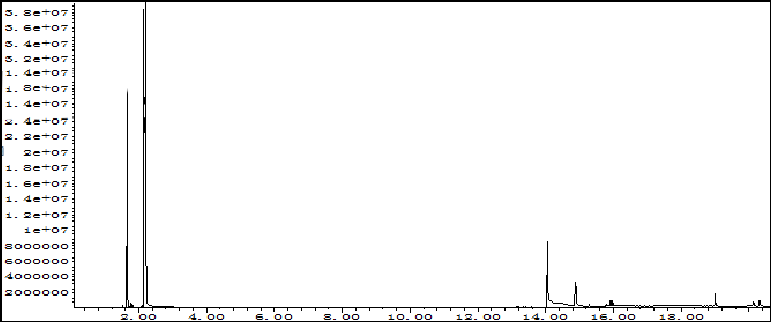
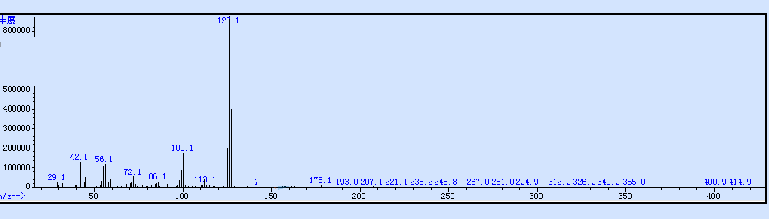
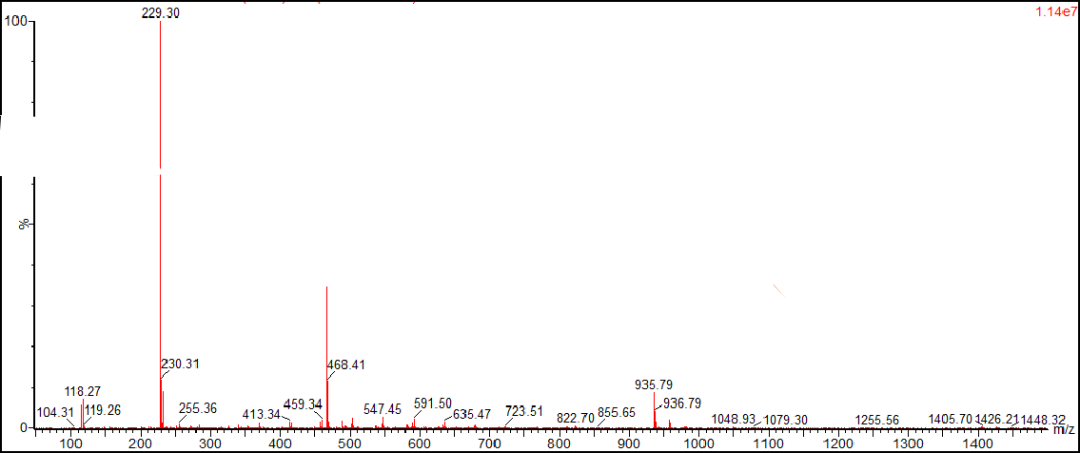
Figure 3 GC-MS spectrum of a mixture
Share to:
Send Inquiry

Mr. James
Tel:0086-371-58651986
Fax:
Mobile Phone:+8613783582233
Email:sales@cn-lubricantadditive.com
Address:No.11 Changchun Road, High-Tech Zone, Zhengzhou, Henan
Related Products List
Mobile Site


Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.