
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
![]() September 29, 2023
September 29, 2023

Black metal (steel) is prone to rust when placed outdoors or in open air conditions, which not only affects the appearance quality, but also affects the normal operation of painting, bonding, and other processes. If not treated in a timely manner, it can even lead to material scrapping and unnecessary economic losses.
Traditional chemical rust removal usually uses strong acids, which can react with rust and metal oxides to form soluble salts, thus achieving the purpose of rust removal. At the same time, the acid can react with the base metal to release hydrogen, which can generate pressure on rust and insoluble oxide skin, which is conducive to their peeling and the reduction of high valent iron, accelerating the pickling process, However, traditional acid treatment methods also have obvious drawbacks: the production of a large amount of hydrogen during the treatment process can cause hydrogen embrittlement in the steel, leading to a decrease in the mechanical properties of the metal and affecting the strength of the steel itself.
The commonly used rust inhibitors in water-based metal working fluids include the following categories:
Petroleum sulfonate
Petroleum sulfonates are typical rust inhibitors, such as T701, T702, T706, etc.
At present, the most commonly used is Sodium Petroleum Sulfonate T702, which has good rust resistance when its molecular weight is around 500g/mol and good emulsification ability when it is around 450g/mol.
Through experiments, it has been confirmed that even using sodium sulfonate with a molecular weight of 460g/mol (with a content of 60%), adding 2% to the concentrated solution can greatly improve the anti rust ability of the formula, which should be based on the synergistic effect of various additives.
T701 and T706 are commonly used in some older cutting fluid formulations and are still in use, but they are no longer mainstream.
Boron containing additives
Boron containing additives mainly include boric acid, borax, boric acid esters, ammonium borate salts, boric acid amides, etc. Boric acid and borax need to be used after reacting with amines.
It shows the use of only boric acid as a rust inhibitor (with a concentration relative to the concentrated solution), a dilution concentration of 3%, and a pH of 9.5 at 35 ℃ × The experimental results of cast iron powder at 24 hours show that the rust prevention ability obtained solely by using boron containing additives as rust prevention components is very average, so it is often used in combination with fatty acid rust inhibitors in practice.
Boric acid ester is a good rust inhibitor, but its economy is not as good as boric acid. It is best to also mix with long-chain carboxylic acid additives when applied. Some relatively simple water-based rust inhibitors are made using borate esters and long-chain fatty acids.
Long chain fatty acids
Long chain fatty acids are mainly C10-12 fatty acids, which are currently the mainstream and most widely used anti rust additives. The longer its carbon chain, the stronger its rust resistance and the weaker its resistance to hard water.
This type of additive needs to be used after reacting with amine, and the higher its content, the better its rust prevention performance.
Sebacic acid
Sebacic acid is generally prepared from castor oil by heating, saponification, and separation after hot cracking. Castor oil is the most deeply processed vegetable oil in the world, and sebacic acid is an important downstream product, widely used as a rust inhibitor for water-based products.
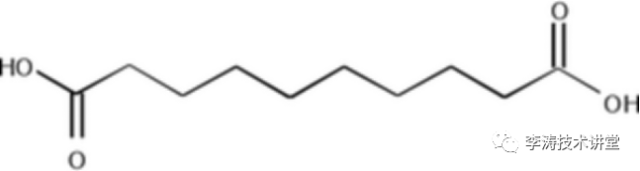
Eleven carbon dicarboxylic acid, twelve carbon dicarboxylic acid
This type of additive has excellent rust prevention performance, and there are also many domestic suppliers. In terms of preparation process, imported products are manufactured by chemical synthesis method, while domestic products are produced by microbial fermentation method. There is no difference in purity between the two, but slight performance differences need to be confirmed through experiments based on specific formulas.
Ternary acid
The chemical name of a ternary acid is 2,4,6-tris (aminohexyl) -1,3,5-triazine, which is manufactured by chemical synthesis and has excellent rust resistance.
In order to reduce production costs and supply prices, the finished product is generally in the form of a wet cake with a content of 50% or 65%, and its dry matter content can be easily detected through the drying method. At present, there are several domestic suppliers and more and more users.
Compared with long-chain dicarboxylic acids and ternary acids, in most cases, there is no significant difference in rust prevention ability between the two types of additives. Ternary acids contain a certain amount of chloride ions, but have no significant impact on the rust resistance of the product.
When using ternary acids, attention should be paid to the hygroscopicity of the additives, and the packaging bag mouth must be sealed for storage.
PTBBA
At present, the existing synthesis methods for p-tert butylbenzoic acid are oxidation synthesis, mainly including solventless oxidation, nitric acid oxidation, liquid-phase catalytic oxidation, potassium permanganate oxidation, microwave synthesis, high-temperature gas-phase oxidation, etc. These methods all use p-tert butylbenzene as the raw material.
Dodecenylsuccinic acid (T746)
Dodecenylsuccinic acid is obtained by reacting with maleic anhydride from superimposed gasoline or tetrapolypropylene as raw materials. Although this type of additive is good in rust prevention, it can seriously reduce the cleaning performance of the cutting fluid, so it should be used with caution.
Amide additives
Amides are commonly produced by heating monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, and carboxylic acid, which are effective rust inhibitors. Low concentration alkyl alcohol amide solutions can prevent steel from rusting and have good hydrolysis resistance.
This kind of additive can be used as co emulsifier and anti rust agent. Pay attention to control foam when using it.
Ntrite
Nitrite is an ancient rust inhibitor with excellent passivation effect on ferrous metals and extremely low cost.
When the concentration of nitrite is very low, it may promote corrosion; Only when a certain concentration is reached can it have a good sustained-release effect. Experiments have shown that in microemulsion cutting fluid, its content of 2% can achieve excellent rust prevention performance in the diluent.
The nitrosamines generated by sodium nitrite under certain conditions are carcinogenic and have been banned! Although there are still many manufacturers using it, it should be controlled.
The above is the Which rust inhibitor is better in water-based processing fluids? we have listed for you. You can submit the following form to obtain more industry information we provide for you.
You can visit our website or contact us, and we will provide the latest consultation and solutions
Send Inquiry
Most Popular
lastest New
Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry

Mr. James
Tel:0086-371-58651986
Fax:
Mobile Phone:+8613783582233
Email:sales@cn-lubricantadditive.com
Address:No.11 Changchun Road, High-Tech Zone, Zhengzhou, Henan
Related Products List
Mobile Site


Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.