
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
![]() January 03, 2024
January 03, 2024
 What is the difference between hot and cold rolling lubricants?
What is the difference between hot and cold rolling lubricants?
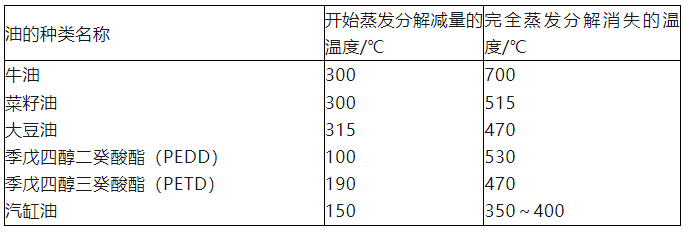
The above is the What is the difference between hot and cold rolling lubricants? we have listed for you. You can submit the following form to obtain more industry information we provide for you.
You can visit our website or contact us, and we will provide the latest consultation and solutions
Send Inquiry
Most Popular
lastest New
Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry

Mr. James
Tel:0086-371-58651986
Fax:
Mobile Phone:+8613783582233
Email:sales@cn-lubricantadditive.com
Address:No.11 Changchun Road, High-Tech Zone, Zhengzhou, Henan
Related Products List
Mobile Site


Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.